AI Prompt Examples
AI Prompt Examples
Astah AI Copilot supports a wide range of modeling tasks through natural conversation. This page provides practical scenarios and prompt examples you can use and adapt for your own projects, including:
- Starting from text requirements and generating diagrams
- Adding elements to existing models
- Analyzing and validating designs
- Explaining complex diagrams in natural language
- Generating documentation
- Working with code via the Astah MCP Server
Use these scenarios as starting points and adjust the prompts to match your domain and modeling needs.
Scenario 1: Designing with AI
Start from Requirements and Generate Diagrams
You can begin with high-level requirements and refine them step-by-step to get better proposals from Copilot.
Example prompts
I want to build an order management system for an e-commerce site.
What functions are needed?
For now, just propose ideas without editing the model.
Copilot may propose functions such as :
- Order entry and processing
- Order fulfillment
- Inventory management
- Payment processing
- Customer management
- Reporting and analytics
- System administration
You can then focus on a specific area and generate a diagram:
Create a class diagram for “2. Order fulfillment”.
→ Copilot generates a class diagram proposal based on the suggested structure.
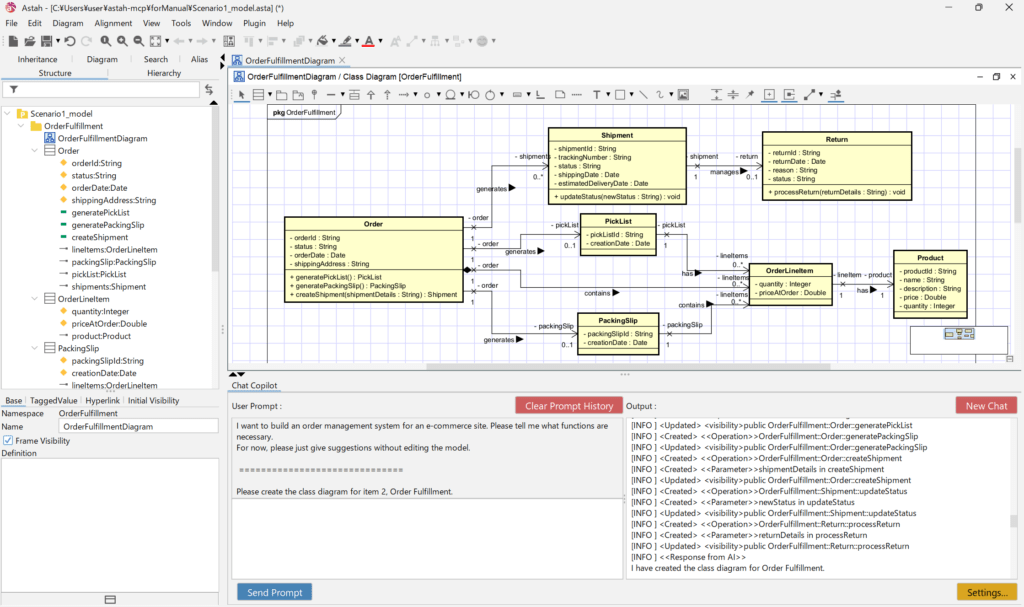
Adding to an existing model
Add a Payment class to the open class diagram, and associate it with the Order class.
→ Copilot analyzes the current diagram and adds the class and relationship in an appropriate place.
Scenario 2: Analyzing and Validating Models
Ask Copilot to review an existing diagram and provide insights about quality and structure.
Example prompt
Point out design issues in the open class diagram.
Copilot may highlight:
- Invalid or inconsistent relationships
- Missing responsibilities
- Potential design smells
- Alignment with principles such as SOLID
Use this as input for refactoring or design reviews.
Scenario 3: Explaining Diagrams in Plain Language
Convert complex diagrams into clear, natural-language explanations.
Example prompt
Explain the processing flow in the open sequence diagram.
→ Copilot describes each step in plain language, heling you:
- Communicate behavior to non-technical stakeholders
- Prepare documentation and reports
- Onboard new team members more quickly
Scenario 4: Generating Code from Models
(Sample of using the Astah MCP Server and an IDE or external AI client)
Copilot can generate code from your diagrams when integrated with external tools through the Astah MCP Server. For setup instructions, see the Astah MCP Server documentation.
Example Prompt
Generate Java code from the open class diagram.
→ Copilot produces Java classes, attributes, and method stubs based on the diagram.
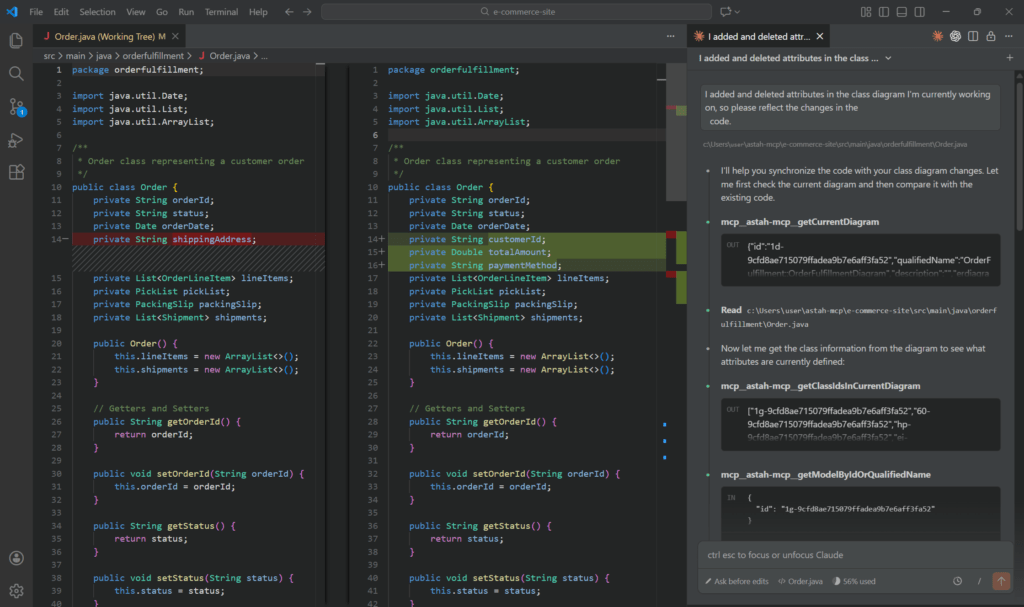
Reflect design changes into code
I added and removed attributes in the open class diagram.
Update the code to reflect these changes.
→ Copilot identifies the modified elements and updates the relevant source code files.
Scenario 5: Reverse Engineering Code into Models
Copilot can analyze source code and generate diagrams directly in Astah.
Example prompt
Create a class diagram from this Java code.
→ Copilot analyzes the code and generates a class diagram with classes and relationships.
For reverse engineering, we have a dedicated plug-in “AI-Powered Code Reverse“.
Scenario 6: Checking Model – Code Consistency
Ensure your design and implementation stay aligned as they evolve.
Example prompt
Check consistency between the open class diagram and the code.
Copilot can identify inconsistencies such as:
- Attributes or classes that exist in the model but not in the code
- Elements present in the code but missing from the model
- Mismatched method signatures or types
This is especially useful during refactoring or when multiple team collaborate on the same system.
Scenario 7: Generating Documentation from ER Diagrams
Generate draft technical documents directly from ER diagrams.
Example prompt
Generate a database design document from the open ER diagram “Order Management System ER Diagram”, including the purpose of each table and descriptions of the relationships.
Copilot may output documentation like this:
Database Design Document for Order Management System ER Diagram
1. Overview
This document describes the database design based on the ER diagram
"Order Management System ER Diagram". It manages information about
customers, orders, order items, products, and payments.
2. Table Definitions
2.1. Customer
Purpose:
Stores customer information used by the system.
Columns:
- customerId: ...
- name: ...
- email: ...
...
You can copy or edit the generated content to create official documentation.
Tips for Better Prompting
- Start simple, then refine.
Begin with a basic request and add details based on Copilot’s response. - Focus each prompt on one task.
For large systems, ask about one diagram, feature, or component at a time. - Reference diagrams explicitly.
For example: “the open class diagram”, “the sequence diagram named Checkout Flow”, etc.
- Use follow-up prompts.
Continue the same conversation instead of restating context:
“Now generate a sequence diagram for the checkout flow based on that class diagram.”
Related Resources
If you have any questions or usecase suggestions, please feel free to share them with us!